Имплантат или имплантант как правильно: Как правильно называются и пишутся дентальные импланты
Разбираемся, как правильно называть дентальные импланты и влияет ли неправильное название на что-либо
Одной из самых передовых и динамично развивающихся отраслей современной стоматологии является имплантология. Сфера охватывает различные методы восстановления утраченных зубов посредством вживления имплантов. После установки они берут на себя весь функционал зубных корней – принимают жевательную нагрузку от коронок или протезов и передают ее костной ткани, в которой активируются обменные процессы и прекращаются атрофические. Для обозначения таких изделий используют разные термины: «импланты», «имплантаты» или «имплантанты». О том, как правильно пишется и произносится название, а какая словоформа является в корне неверной, читайте далее в статье.
«Имплант» и «имплантат» – что означают эти термины и в чем разница
Понятия являются равнозначными по смыслу. Эти слова описывают один и тот же предмет, несмотря на разницу в написании и произношении. Все дело в том, что сами термины мы «одолжили» из разных языков. Так, слово «имплант» произошло от английского глагола «to implant», перевод которого звучит как «вживлять». Термин «имплантат» был заимствован из французского языка, пошел от существительного «implant», что на русском звучит как «трансплантат». Более правильным считается термин «имплант», хотя «имплантат» также является допустимой формой, просто чаще употребляется в разговорной речи.
В стоматологии имплантом называют изделие, которое вживляется в костную ткань или лунку сразу после удаления зуба, берет на себя все функции зубного корня и обеспечивает надежное удержание протеза на своем месте. Такие изделия создают из чистого титана или с незначительными примесями – материал являются абсолютно биосовместимым и лучше всего приживается в живой ткани.
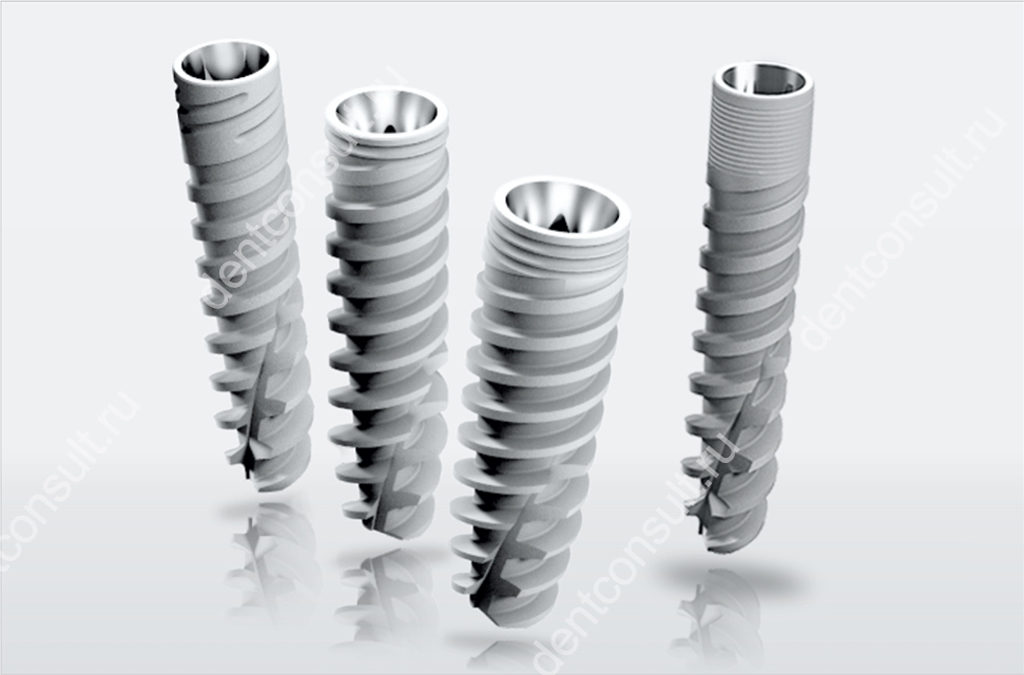

 В стоматологии имплант – это изделие, которое вживляется в костную ткань
В стоматологии имплант – это изделие, которое вживляется в костную тканьОсновное назначение имплантов – для чего они нужны
Титановые зубные корни вживляют в тех случаях, когда провести полноценное восстановление зуба иными методами уже невозможно – если не сохранился живой корень или он слишком сильно поврежден и требует удаления. В таком случае оптимальным решением проблемы будет его полная замена искусственным аналогом, на который впоследствии можно поставить полнофункциональную коронку. К тому же импланты применяются в качестве опорных элементов под «мосты», частичные или полные протезы, если в ряду не хватает больше одного зуба.
Имплантация в классическом исполнении требует довольно много времени. Восстановление проводится в два самостоятельных этапа:
- сначала пациент проходит всестороннее обследование и сдает необходимые анализы. Специалисты тем временем тщательно изучают клиническую картину и прорабатывают возможные варианты лечения, планируют процедуру, выбирают модели титановых корней и подходящие места под их вживление. Уже в рамках процедуры хирург вживляет импланты, сверху фиксирует специальные заглушки и ушивает десну. Далее потребуется около 3-4 месяцев для нижней челюсти и до 6 месяцев для верхней, чтобы изделия полностью прижились в толще костной ткани. Иногда при одиночных реставрациях временные коронки фиксируют сразу, чтобы устранить эстетический дефект на время приживления,
- второй этап лечения наступает уже после полной остеоинтеграции титановых корней. Специалист снимает заглушки, после чего фиксирует формирователи десны на две недели (для фронтальной группы зубов, чтобы сформировать ровный десневой контур) или сразу абатменты, на которые ставит постоянные коронки, частичный или полный протез.
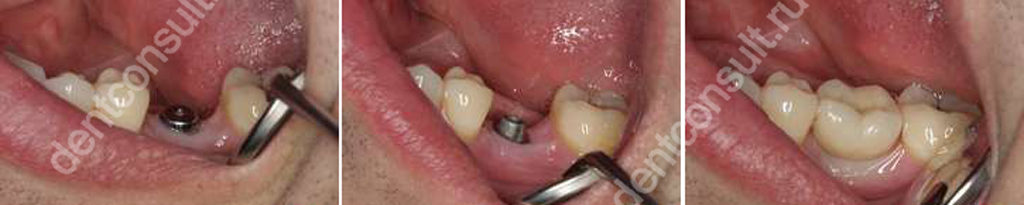
 При двухэтапном методе процесс установки ипмлантов может длится несколько месяцев
При двухэтапном методе процесс установки ипмлантов может длится несколько месяцевНо есть и другая альтернатива – одноэтапная имплантация. Этот термин объединяет множество различных методик, каждая из которых предполагает возможность протезирования сразу или в самом скором времени после установки имплантов. Одним из таких протоколов является одномоментная концепция, в рамках которой изделие погружают в лунку сразу после удаления зуба, а поверх фиксируют коронку.
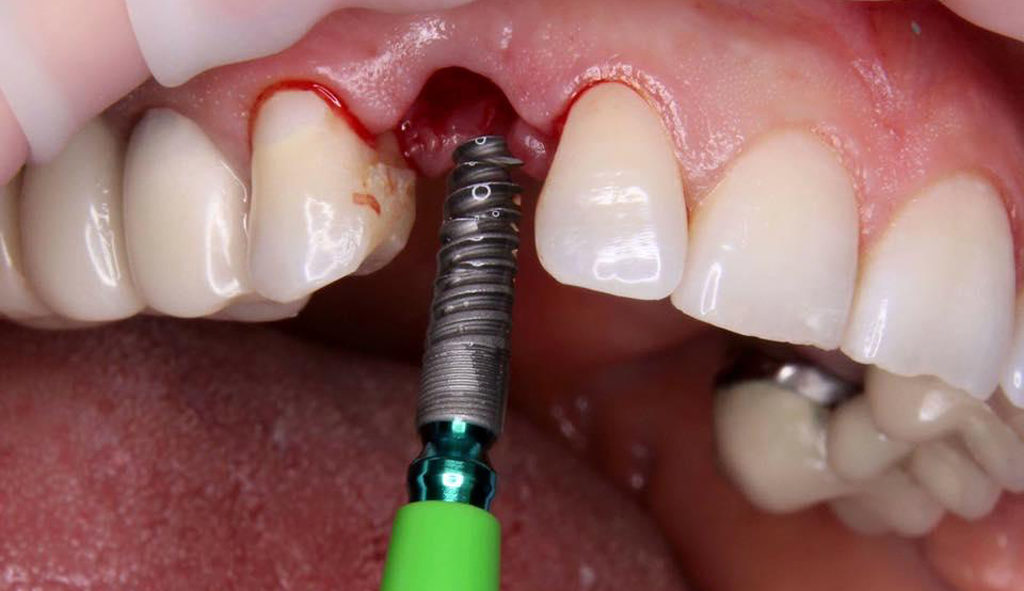
 На фото показана установка импланта сразу после удаления зуба
На фото показана установка импланта сразу после удаления зубаПеред лечением пациент обязательно проходит подготовку. Наряду с обследованиями, рентген-диагностикой и анализами придется залечить все кариозные дырочки во рту, устранить острые воспалительные процессы. Если имеют место такие патологии, как пародонтит и пародонтоз, сперва необходимо пройти их комплексное лечение, чтобы добиться стойкой ремиссии. В некоторых случаях, в частности при применении классического метода, обычно приходится предварительно проводить костную пластику или синус-лифтинг, если речь идет о реставрации верхней челюсти. Одноэтапные протоколы зачастую позволяют избежать этого этапа, а значит, ускорить сам процесс лечения и сэкономить на дорогостоящем наращивании челюстной кости.
Что именно означают эти термины
Чтобы понять и запомнить, как правильно говорить: «имплант» или «имплантат», нужно немного углубиться в семантику этих терминов. Ниже подробно разъяснены значения каждого из слов:
- по одной из версий, слово «имплант» пришло к нам из английского языка, образовалось от глагола «to implant», то есть «вживлять», «пересаживать»,
- «имплантат» мы позаимствовали из французского языка, где существительное «implant» переводится как трансплантат.
 «Имплант» и «имплантат» – это равнозначные понятия
«Имплант» и «имплантат» – это равнозначные понятияНельзя сказать, чем отличаются по смыслу слова «имплант» и «имплантат», поскольку это равнозначные понятия, и никакой смысловой разницы между ними нет. Первый термин является более правильным, но второй давно и прочно вошел в обход, в том числе в профессиональных кругах. Его употребление также не будет считаться ошибкой. Сложнее дела обстоят с понятием «имплантант» – подробнее об этом в следующем разделе.
Пишем правильно: «имплант» или «имплантант»
Иногда вместо правильного произношения можно услышать формулировку «имплантант». Когда этим словом называют титановый корень, служащий опорой для восстановления отсутствующего зуба, – это большая ошибка.
«Я так однажды опозорился. Непонятно с чего решил, что правильно будет имплантант, и в разговоре с одним врачом исправил его на свою голову. Стыдоба настоящая! Хорошо, что человек понимающий попался, спокойно мне все объяснил и не стал высмеивать. Я с того момента на всю жизнь запомнил, что имплантантом можно врача назвать, и то с натяжкой. Но уж точно не тот стержень, который в десну вживляют…»
OlegMi, из переписки на форуме www.32 top.ru

 Имплантантом можно назвать человека осуществляющего имплантацию
Имплантантом можно назвать человека осуществляющего имплантациюПо правилам русского языка, окончания «-ат, -ант» обозначают не предмет, а человека или одушевленное существительное, выполняющее какое-либо действие или имеющего к нему непосредственное отношение. Такие окончания часто можно встретить в словах, определяющих принадлежность человека к той или иной профессии, конкретному роду деятельности: «диверсант» – тот, кто совершает диверсии, «музыкант» – тот, кто пишет или воспроизводит музыку и т.д.
Профессия имплантант или имплантанолог
Исходя из выше сказанного, логично предположить, что истинное значения термина «имплантант» – специалист, который проводит операции по имплантации. Это стоматолог конкретной специализации, который занимается восстановлением утраченных зубов посредством установки имплантологических систем и дальнейшего протезирования. Для описания этого рода деятельности есть более подходящие и благозвучные термины: «имплантолог», «хирург-имплантолог».
- Параскевич В.Л., Дентальная имплантология, 2002.
Конструкции для восстановления зубов могут называть по-разному – имплант, имплантат, имплантант. Только вот какое из этих понятий правильной и как в действительности называются эти изделия. Ведь нередко многие врачи называют эти элементы разными названиями. Конечно, для многих пациентов все равно как правильно называются системы для восстановления зубов, для них важнее качество оказанной услуги. Но все же, какое из этих понятий верное?
Как правильно имплант или имплантант?
Несмотря на то, что во многих рекламах различных стоматологических клиник, на различных медицинских сайтах, порталах применяются три понятия для обозначения одного и того же изделия, это немного неправильно. А для того чтобы понять в чем ошибка, стоит внимательно рассмотреть что обозначают термины – имплант и имплантант.
Что такое имплант и имплантат

Зубные импланты, имплантанты – все это искусственные конструкции, заменяющие отсутствующие зубы. Они фиксируются в костной ткани челюсти и служат надежной опорой для несъемных или съемных зубных протезов.
Понятия имплант и имплантат являются одинаковыми. Они обозначают одно и то же изделие, только имеют отличия в написании. Это заимствованные понятия. Первое слово происходит от английского понятия – to implant, что в переводе обозначает – «вживлять». Второй термин произошел от французского implant, который переводится «трансплантат».
Наиболее часто применяется понятие имплант, именно так нужно правильно произносить это слово. Но может также применяться и второе понятие – имплантат.
Само слово имплант обозначает изделие, которое используется в виде протезированного элемента для замены определенного органа человека.
Внимание! Имплант в стоматологической сфере это штучный корень, который вживляется в область костной ткани. Затем на этот элемент производится установка протезного элемента или коронки. Этот элемент производится только из титана. Именно титан полностью подходит для человеческой ткани.
Для чего предназначены импланты?
Импланты часто используют в следующих случаях:
- в качестве восполнения зубного ряда при потере одного зуба;
- применяется в качестве опоры для обеспечения требуемой устойчивости протезных элементов съемного или несъемного типа;
- для сохранения красоты улыбки и здорового состояния соседних зубов.

Имплант — это искусственный титановый «корень», который хирургическим путём устанавливается в кость челюсти, где раньше был зуб пациента.
Обычно процедура восстановления зубов занимает достаточно длительный период. Она, как правило, проводится в несколько этапов. При двухэтапной имплантации выполняются следующие процедуры:
- На начальном этапе проводится вживление импланта;
- Для того чтобы вставить имплант в костную ткань, в ней просверливается лунка;
- Далее через некоторое время устанавливается абатмент;
- Врач может сначала установить временную коронку, а затем уже постоянную.
Стоит учитывать, что двухэтапная имплантация достаточно длительная, она может занять примерно 3-4 месяца, именно за этот период происходит полное срастание импланта с костной тканью.
Если пациенту нужно срочно установить имплант, то может в качестве альтернативы быть предложена одноэтапная имплантация. Она проводится намного быстрее, всего за 7 дней. Установка импланта может проводиться сразу же после удаления зуба. Затем проводится установка абатмента, а на него уже устанавливается временная коронка.
Важно! Перед проведением вживления титанового корня рекомендуется пройти полное обследование у стоматолога. При осмотре врач сможет полностью осмотреть полость рта, состояние зубов и выявить заболевания. При наличии кариеса и других патологических процессов зубов, обязательно нужно провести полное лечение всех этих недугов.
На момент проведения имплантации ротовая полость должна быть здоровой. Обязательно нужно пролечить десна, они не должны быть воспаленными, иначе может возникнуть отторжение титанового корня.Благодаря имплантам можно полностью восполнить не только функции утраченных зубов, но и обеспечить эстетику внешности зубного ряда. Корни из титана отлично приживаются. Но после их установки обязательно нужно тщательно соблюдать гигиену, это поможет продлить их срок службы и сохранить их на длительное время.
Что такое имплантант?

Имплантолог – это врач-стоматолог, который фиксирует съёмный протезы, восстанавливая утраченный зуб. К нему обращаются, когда по причине рассасывания костной ткани становится невозможным ношения съёмных протезов без создания дополнительных точек опоры.
Иногда импланты или имплантаты называют имплантантами. А вот правильно это? Нет, это неправильно. В соответствии с правилами русского языка, окончание –ант указывает не на предмет, а на человека или на лицо, которое оказывает какие-то действия. В этом случае имплантантом можно назвать врача, который производит установку имплантов, также его называют имплантологом.
Именно стоматолог-имплантолог восстанавливает полностью утраченные или полуразрушенные зубы. Он обеспечивает полное восстановление целостности зубного ряда. Его услуги могут понадобиться тогда, когда у пациента наблюдается полная или частичная потеря зубов.
Услугами имплантолога можно воспользоваться, когда необходимо восстановить один утраченный зуб или создать опору для установки мостовидных или съемных изделий. Зачастую при установке больших протезированных конструкций требуется удаление или обточка соседних зубов. А вот при имплантации этих жертв выполнять не требуется.
В любом случае при потере одного или нескольких зубов независимо от их зоны расположения важно воспользоваться услугами имплантолога как можно раньше. На приеме он сможет оценить состояние зубов и сам подберет необходимый вид системы для имплантации. При помощи услуг имплантолога и имплантации можно предотвратить опасные последствия для всей полости рта и зубного ряда – искривление челюсти, нарушение прикуса, изменение овала лица, а также различные эстетические дефекты.
как правильно говорить, значение терминов
В стоматологии большой популярностью пользуется отрасль, которая занимается восстановлением утраченных зубов. В связи с этим употребляют такие слова, как «импланты», «имплантаты» или «имплантанты» — как правильно говорить, зависит от контекста, в котором фигурирует тот или иной термин. Ведь каждый из них имеет собственное значение. Давайте разберёмся.
Значение терминов
Углубившись в недра семантики, можно понять, как правильно говорить — имплант или имплантат.
- Имплант — слово родом из Франции, переводящееся как «трансплантат». Оно служит для обозначения протеза зуба. В английском языке присутствует слово «implant», оно расшифровывается как «вживление» и «пересадка».
- Имплантант имеет концовку «-ат, -ант», обозначающую действие. Она присутствует в таких словах, как «диверсант» (человек, обеспечивающий создание диверсий), «арестант» (человек, находящийся в тюрьме). Аналогично и термин «имплантант» подразумевает человека, который устанавливает зубные протезы (иными словами — это стоматолог).
- Имплантат — разговорный вариант слова, сформировавшийся в результате неправильного произношения слова «имплант» (возможно, причиной путаницы послужило слово «трансплантант», по аналогии с которым и стали добавлять лишний суффикс).
Таким образом, вопрос о том, как правильно — «имплант» или «имплантат» — не совсем корректен. Поскольку второй термин уже прочно вошел в стоматологическую терминологию, его употребление грубой ошибкой не является. Можно говорить «импланты», «имплантаты» или «имплантанты», но следует помнить, что два первых термина обозначают зуб, а третий — человека.
Что такое имплант
В русском языке прижились первые два термина. Медики называют зубной протез «имплант» и «имплантант», несмотря на то что второй вариант некорректен.
Имплант — это винт, изготавливаемый из высокопрочного материала, диаметром 2−3 мм. Этот корень используется для вкручивания в надкостницу или кость на том участке, где ранее был коренной зуб.


На изображении он обозначен как титановый корень, который является основой для крепления зубной коронки.
Имплант показан к применению в ряде ситуаций:
- Необходимость в опоре для съемных и несъемных протезов;
- Если требуется замена одного удаленного зуба;
- Когда больной желает сохранить эстетическую привлекательность улыбки и зубы, расположенные рядом с пораженным участком.
Для того чтобы восстановить зубы с применением имплантов, потребуется много времени, в течение которого пациент проходит несколько этапов:
- Доктор устанавливает искусственный металлический корень;
- Поврежденные ткани десен должны полностью восстановиться за несколько месяцев;
- Сверху корня вживляется специальная конструкция под названием «абатмент», по прошествии двух недель на неё устанавливают керамическую или металлическую коронку.


Классическая схема
В современных стоматологических клиниках пациенту предлагают альтернативный метод восстановления — одномоментная имплантация (её также называют одноэтапная). Её особенность состоит в том, что если при обычном протезировании, доктор ожидает полного заживления лунки, то здесь имплант вживляется сразу после удаления — в углубление, оставшееся после удаления зуба, вставляют корень из титана. Как правило, длительность выполнения такой методы составляет всего 7 дней, в течение которых будет произведено удаление коренного зуба и установка на его место импланта.


Одноэтапная имплантация
Но перед тем как будет вживляться титановый корень, стоит пройти качественное обследование у стоматолога. Во время осмотра доктор должен детально изучить состояние ротовой полости. В случае обнаружения заболеваний, в обязательном порядке назначается лечение. Если этого не сделать, то титановый корень не приживется и может стать причиной развития дополнительной негативной симптоматики.
Такие изделия, как импланты, обладают массой преимуществ, главное из которых заключается в отсутствии необходимости удалять и обтачивать зубы, чтобы установить протезы. Кроме того, с помощью имплантов можно с легкостью и в короткие сроки устранить единичный дефект.
Считается, что отсутствие хотя бы одного зуба вызывает рыхлость тканей и появление такой патологии, как подвижность. Постепенно соседние зубы будут двигаться к свободному пространству, в результате чего между ближайшими элементами появятся щели. А это спровоцирует возникновение воспалительных и кариозных процессов.
Профессия: имплантант или имплантанолог?
Имплантант, или имплантанолог — это доктор, который осуществляет восстановление единичных зубов или их полного ряда.
Имплантанта иногда путают с протезистом. Их функции неодинаковы, но взаимосвязаны. Благодаря врач-имплантологу создается опора для протезов мостовидного или съёмного типа.
Перед началом работы доктор определяет подробную схему терапии, где указываются сроки приживления винта. Если человек принял решение обратиться за помощью к имплантанту, то предпочтение стоит отдать методике восстановления зубов, предложенной доктором Данте. Её особенность заключается в отсутствии какого-либо хирургического вмешательства: производится простое ввинчивание импланта в канал, где ранее располагался коренной зуб.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как сказать правильно — импланты или имплантанты?
Представьте, что и первый, и второй варианты неверны, причем если вариант «имплант» еще допустим в разговорной речи или в профессиональном сленге врачей, то «имплантант», «имплантанты» — явная ошибка.
Правильно говорить «импланта́т», «импланта́ты», «импланировать».
Для начала давайте разберемся, что же такое зубной имплантат. Имплантат — это небольшой металлический винт, который интегрируется в верхнюю или нижнюю челюсти и выполняет роль корня потерянного зуба для дальнейшего протезирования, восстановления и построения зубного ряда.
Слово «имплантат» пришло к нам из немецкого, а в немецкий — из латинского языка и означает что-то, вставляемое внутрь: im — «в», plantare — «сажать». Имплантаты бывают не только дентальные, или зубные, но и кохлеарные, стволомозговые, сердечные, имплантаты сетчатки и даже идентификационные имплантаты. Последний в качестве микрочипа с уникальным электронным кодом встраивается под кожу домашних любимцев, чтобы они никогда не терялись.
В английском языке также есть слово implant, означающее: внедрять, вживлять, насаждать, сажать. Русская калька с английского произносится «имплант». Это слово также допустимо в русском разговорном языке, мы часто слышим его в профессиональном языке врачей-стоматологов и медицинской документации. Если учесть то, что слово «имплантат», «имплант» относительно недавно стало активно использоваться в русском языке, можно ожидать, что с годами произойдет определенная редукция, или упрощение термина «имплантат», и «имплант» станет официальной языковой и литературной нормой. Однако сегодня, повторим, официальный грамматический словарь русского языка поддерживает только одно правописание — «имплантат».
В стоматологии «Скаковский» высококвалифицированные специалисты с большим опытом работы выполнят любые виды работ, связанных с зубной имплантацией. Цены на имплантаты зубов у нас одни из самых низких в городе Сочи, при этом качество всегда остается на высоте.
«Как ставят импланты зубов?» – Яндекс.Кью
Имплантация зубов — не такой сложный, долгий или болезненный процесс, как считают многие пациенты. Для такого лечения нужно несколько визитов к стоматологу. Обычно его выполняют в пять этапов.
Консультация и диагностика. На первом приеме врач оценивает состояние полости рта и возможность установки имплантов. Он выполняет диагностические снимки, слепки, предлагает пациенту варианты имплантации, подбирает конструкции для нее, определяет, как именно они будут устанавливаться.
Подготовка. До процедуры нужно провести санацию полости рта: у пациента не должно быть кариеса, воспалений, других заболеваний. Это важно, чтобы исключить риск осложнений или отторжения импланта. В редких случаях требуется дополнительное лечение. Это может быть коррекция прикуса (нужна, если соседние зубы уже начали смешаться в сторону промежутка, закрывать его, и для установки импланта нужно освободить место). Если костной ткани недостаточно, чтобы надежно установить имплант, проводят костную пластику (установка мембран или костных блоков выполняется за один визит к имплантологу).
Установка импланта. Проводится с полным обезболиванием, занимает не более одного часа, чаще — около 20-30 минут. Поверх конструкции может устанавливаться временная коронка, чтобы закрыть промежуток в зубном ряду на время лечения.
Установка формирователя десны, абатмента. Это — вспомогательные конструкции, которые нужны для дальнейшего протезирования. Формирователь десны заполняет место в лунке, помогает подготовить ложе для размещения искусственной коронки. Его ставят на несколько недель, а затем снимают, устанавливая на его место абатмент — конструкцию, которая соединит имплант с коронкой.
Протезирование. Установка постоянной коронки или протеза выполняется, когда завершена остеоинтеграция, имплант прижился и может нести полноценную жевательную нагрузку. Их закрепляют с помощью механического соединения и с использованием стоматологического цемента. Процедура проводится быстро, за один визит к стоматологу.
В стоматологии «ДентоСпас» имплантация проводится без боли, с помощью надежных имплантов, с качественным результатом. Узнать больше о таком лечении можно на сайте клиники.
Как правильно имплантаты или имплантанты
Как правильно пишется и говорится имплант, имплантант или имплантат
Конструкции для восстановления зубов могут называть по-разному – имплант, имплантат, имплантант. Только вот какое из этих понятий правильной и как в действительности называются эти изделия. Ведь нередко многие врачи называют эти элементы разными названиями. Конечно, для многих пациентов все равно как правильно называются системы для восстановления зубов, для них важнее качество оказанной услуги. Но все же, какое из этих понятий верное?
Как правильно имплант или имплантант?
Несмотря на то, что во многих рекламах различных стоматологических клиник, на различных медицинских сайтах, порталах применяются три понятия для обозначения одного и того же изделия, это немного неправильно. А для того чтобы понять в чем ошибка, стоит внимательно рассмотреть что обозначают термины – имплант и имплантант.
Что такое имплант и имплантат
Зубные импланты, имплантанты – все это искусственные конструкции, заменяющие отсутствующие зубы. Они фиксируются в костной ткани челюсти и служат надежной опорой для несъемных или съемных зубных протезов.
Понятия имплант и имплантат являются одинаковыми. Они обозначают одно и то же изделие, только имеют отличия в написании. Это заимствованные понятия. Первое слово происходит от английского понятия – to implant, что в переводе обозначает – «вживлять». Второй термин произошел от французского implant, который переводится «трансплантат». Наиболее часто применяется понятие имплант, именно так нужно правильно произносить это слово. Но может также применяться и второе понятие – имплантат.
Само слово имплант обозначает изделие, которое используется в виде протезированного элемента для замены определенного органа человека.
Внимание! Имплант в стоматологической сфере это штучный корень, который вживляется в область костной ткани. Затем на этот элемент производится установка протезного элемента или коронки. Этот элемент производится только из титана. Именно титан полностью подходит для человеческой ткани.
Для чего предназначены импланты?
Импланты часто используют в следующих случаях:
- в качестве восполнения зубного ряда при потере одного зуба;
- применяется в качестве опоры для обеспечения требуемой устойчивости протезных элементов съемного или несъемного типа;
- для сохранения красоты улыбки и здорового состояния соседних зубов.
Имплант — это искусственный титановый «корень», который хирургическим путём устанавливается в кость челюсти, где раньше был зуб пациента.
Обычно процедура восстановления зубов занимает достаточно длительный период. Она, как правило, проводится в несколько этапов. При двухэтапной имплантации выполняются следующие процедуры:
- На начальном этапе проводится вживление импланта;
- Для того чтобы вставить имплант в костную ткань, в ней просверливается лунка;
- Далее через некоторое время устанавливается абатмент;
- Врач может сначала установить временную коронку, а затем уже постоянную.
Стоит учитывать, что двухэтапная имплантация достаточно длительная, она может занять примерно 3-4 месяца, именно за этот период происходит полное срастание импланта с костной тканью. Если пациенту нужно срочно установить имплант, то может в качестве альтернативы быть предложена одноэтапная имплантация. Она проводится намного быстрее, всего за 7 дней. Установка импланта может проводиться сразу же после удаления зуба. Затем проводится установка абатмента, а на него уже устанавливае
Имплантат или имплантант — как правильно?
Имплантант, имплант, имплантат – такими обозначениями обычно называют конструкции, с помощью которых восстанавливают зубы. Какой из этих терминов верный?
Пациенты, заинтересованные в имплантации, могут встретить несколько обозначений конструкции, восстанавливающей зубы. Разные варианты используют даже сами врачи. Конечно, для некоторых принципиального значения точность терминологии не имеет, но как же правильно: имплантат, имплант или имплантант? Или это одно и то же?
Имплант — терминология
Несмотря на то, что в рекламках разнообразных стоматологических клиник и на медицинских порталах все три термина зачастую используются для обозначения одного и того же предмета, это является небольшой ошибкой.
Что такое «имплант»
В большинстве случаев «имплант» и «имплантат» — просто чуть разные по написанию обозначения одного предмета. Оба термина – заимствованные. Первый пришел от английского to implant – вживлять. Второй – от французского implant, что в переводе означает «трансплантат». Чаще используется слово «имплант», так говорить – правильно. Но употреблять можно и другой вариант.
Непосредственно имплант – изделие, которое является протезом и должно заменять какой-нибудь орган человеческого организма. В стоматологии так называют штучный зубной корень, на который будет установлен зубной протез или коронка. Изготавливается он из титана – материала, который биосовместим с человеческим организмом.
Предназначение
Не обойтись без искусственной замены в нескольких случаях. Так, имплант необходим если:
- необходимо заменить один потерянный зуб;
- необходима опора для достаточной устойчивости съемных или несъемных протезов;
- важно сохранить эстетику улыбки и здоровье «соседних» зубов.
Как правило, процесс восстановления зуба занимает достаточно долгий срок. Сначала вживляется сам имплант – искусственный корень, а пациенту придется «выжидать» время, пока не восстановятся ткани десны. Потом в корень вживляется абатмент – посредник, на который еще через пару недель будет установлена металлическая или керамическая коронка.
В качестве альтернативы некоторые стоматологии готовы предложить более быструю одномоментную имплантацию. Если обычная имплантация проводится через некоторое время после удаления зуба, то одномоментная проведена может быть еще до заживления лунки. Сразу после удаления в получившееся углубление вставляется титановый корень, а на абатмент ставится временная коронка.
Перед процедурой имплантации пациенту необходимо посетить стоматолога. Важно избавиться от кариеса и удалить те зубы, которые невозможно вылечить или восстановить. Озаботиться придется и состоянием десен: если они воспалены – повышается риск заражения или отторжения титанового корня.
Благодаря импланту можно полностью восстановить не только эстетические, но и функциональные функции зуба. Титановые корни отлично приживаются, а при должном уходе и соблюдении некоторых мер предосторожности прослужат искусственные зубы не один десяток лет.
А что такое «имплантант»?
Как правильно: импланты или же имплантанты? В некоторых случаях импланты называют имплантантом. Правильно ли это? Нет. Согласно правилам русского языка окончания –ант обычно указывают на лицо, производящее определенные действия. В данном случае имплантантом можно называть врача-имплантолога, который будет заниматься установкой искусственных зубов.
Именно стоматолог-имплантолог будет заниматься восстановлением целостности зубного ряда. Необходимы его услуги в том случае, если пациент страдает от полной или частичной потери зубов. Альтернативным вариантом выступает стоматолог-протезист, но к его услугам прибегнуть можно далеко не всегда.
Незаменим имплантолог в том случае, если восстановить необходимо штучный «пробел» зубного ряда или создать опору для мостовидного или съемного протеза. Одиночный дефект восстановить гораздо проще и дешевле. Кроме того, для протезов иногда приходится удалять или обтачивать абсолютно здоровые зубы. Установка импланта проводится без подобных жертв.
Зубы, находящиеся в «зоне улыбки», несут важную эстетическую функцию, и многие люди не смогут чувствовать себя комфортно, если имеется хотя бы один «пробел». Не стоит при этом уменьшать и важность жевательных зубов, даже несмотря на то, что их отсутствие может быть абсолютно незаметным для окружающих.
Когда из общего ряда выпадает хотя бы один зуб, его соседи получают большую жевательную нагрузку. Влияет она и на десны: увеличивается риск развития пародонтоза.
Мягкие ткани становятся более рыхлыми, появляется подвижность корней. Со временем зубы могут постараться занять свободное место, начнут образовываться едва заметные щели. Именно такие места предпочитают кариозные воспаления.
В связке с хирургом-имплантологом нередко работают имплантолог-ортопед, пародонтолог, стоматолог-ортопед и терапевт. Только после того, как будет получена полная клиническая картина состояния ротовой полости, можно думать об установке имплантов. Имплантолог должен представить пациенту план, в котором будут расписаны все сроки – от длительности приживления искусственного корня до продолжительности изготовления коронки.
Загрузка…90000 Dentures vs Dental Implants — Comparison of Costs & Benefits 90001 90002 Losing teeth can be quite distressing. Considerations such as replacement cost, convenience, your health and longevity may cause analysis paralysis, but it is important to replace them as soon as possible so you can eat and talk normally and to restore aesthetics and self-confidence. 90003 90002 Your restoration options include both dentures and dental implants, but which one is the best choice for your situation? The following guide is a comparison of the two and will help make your decision a little easier.90005 90006 In This Guide 90007 90003 90009 What are Removable Complete & Partial Dentures? 90010 90002 Dentures are removable appliances that replace missing teeth as well as some of the gum tissue. Complete or full dentures replace all the teeth in the upper or lower jaw, or in both jaws, while partial dentures are used to fill in gaps when some of the natural teeth still remain. 90003 90002 90014 90014 90003 90002 Complete dentures rest directly on the gums, whereas partial dentures are supported by clasps around existing teeth or with precision attachments that are fitted onto crowns.Dentures have a pink gum colored acrylic base that supports the denture teeth. Some dentures will include a lightweight metal framework for extra strength and support. 90005 90019 90019 90003 90009 What Are Dental Implants? 90010 90002 A dental implant is a titanium post that is inserted into the jawbone, replicating the root of a natural tooth. The implant post osseointegrates or bonds strongly with the jawbone, creating an anchor which is used to hold a replacement tooth. They can be used to replace single or multiple teeth, supporting crowns, bridges and even dentures.90003 90009 What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Dentures Compared to Implants? 90010 90028 90029 90030 90031 90032 90031 Dentures 90032 90031 Implants 90032 90037 90038 90039 90030 90041 Jawbone 90042 90041 Bone loss over time can lead to further deterioration of facial structure 90042 90041 Helps stimulate and preserve remaining jawbone to maintain facial structure 90042 90037 90030 90041 Support 90042 90041 Sits on gums — can slip around and cause discomfort 90042 90041 Fixed to jawbone like natural teeth 90042 90037 90030 90041 Longevity 90042 90041 Typically last 7 to 15 years 90042 90041 Long-lasting solution 90042 90037 90030 90041 Cost 90042 90041 Less expensive, but often less effective 90042 90041 Higher up front cost, but better value in the long term.90042 90037 90030 90041 Feeling 90042 90041 Take time to get used to — can feel fake and bulky 90042 90041 Feel and function like natural teeth 90042 90037 90030 90041 Appearance 90042 90041 Can be noticeable if they come loose or cause discomfort 90042 90041 Look close to the real thing. Supports your cheeks and lips 90042 90037 90030 90041 Maintenance 90042 90041 Need to removed regularly for cleaning 90042 90041 Brush and floss same as for regular teeth 90042 90037 90030 90041 Speech 90042 90041 May interfere with speech 90042 90041 No issues 90042 90037 90030 90041 Eating 90042 90041 Have to avoid certain hard or sticky foods 90042 90041 Helps restore chewing ability — removing food limitations 90042 90037 90030 90041 Invasiveness 90042 90041 No surgery required 90042 90041 1 or 2 invasive surgeries 90042 90037 90120 90121 90122 Benefits of choosing dentures include: 90123 90002 90006 Can Closely Match Gum Color 90007 90005 Replacement teeth will look quite natural as modern denture teeth come in many different shapes, sizes and shades.The pink acrylic used to replicate your gum tissue can be closely matched to your natural gum color. 90003 90002 90006 Affordable 90007 90005 Dentures are the more affordable option, particularly if you need to replace multiple teeth. 90003 90002 90006 Non-Invasive 90007 90005 The process for making dentures is non-invasive and unlike implants does not require any surgery. 90003 90002 90006 Easy to Adjust 90007 90005 Dentures are easy to adjust and modifications can be made to accommodate further tooth loss.90003 90002 90006 Support Face Structure 90007 90005 Correctly made dentures will support the cheeks and lips, restoring height between the upper and lower jaws so the face no longer looks as if it has collapsed inwards. 90003 90122 Drawbacks of selecting dentures include: 90123 90002 90006 Not as Natural Looking 90007 90005 They do not look quite as natural as implants since they display acrylic instead of actual gum tissue. 90003 90002 90006 Higher Maintenance 90007 90005 They need to be removed and cleaned regularly, and must be left out of the mouth overnight to give the gums a chance to recover.90003 90002 90006 Can Shift Around 90007 90005 Dentures can sometimes slip around, particularly if they have been worn for a few years as the jawbone changes shape, becoming flatter and less able to provide retention. Messy and expensive denture adhesives only provide a temporary solution. 90003 90002 90006 Harder to Talk With 90007 90005 Some people find it difficult to get used to speaking and eating with dentures and may lack the muscle control required to hold them in place. 90003 90002 90006 Can not Eat Certain Foods 90007 90005 There are restrictions on the types of foods that can be eaten.These restrictions may make it more difficult to have a balanced diet that provides all the nutrients required for good overall health. 90003 90002 90006 They Trap Food 90007 90005 Dentures tend to trap food which can increase the risk of gum disease and decay of remaining teeth. 90003 90002 90006 Fragile 90007 90005 Dentures can be quite fragile and are likely to break if dropped. 90003 90002 90006 Not Permanent 90007 90005 They usually need to be replaced every three to six years (versus 15-20 + years for implants), although those with a metal framework and which are supported by natural teeth may last a little longer.90003 90002 90006 Removable 90007 90005 Some people have a psychological aversion to wearing dentures and would prefer not to have removable teeth. 90003 90002 90006 Can Weaken Surrounding Teeth 90007 90005 Partial dentures can weaken the natural teeth supporting them, and it may be necessary for these teeth to be re-shaped or adapted slightly to accommodate the dentures clasps. 90003 90009 Other Factors to Consider 90010 90002 90006 Insurance coverage 90007 90005 Dentures are generally covered by most dental insurance plans, and your insurance may pay between 15% and 50%.Dental implants are often classified as a cosmetic procedure, so the costs are not typically covered. It is worth checking with your provider as it is possible your insurance might cover a portion of the implant crown, bridge or denture. 90003 90002 90006 Durability 90007 90005 Implants that are properly cared for can last for many years, or even for life, so costs can be lower in the longer term. In comparison, dentures will need replacing relatively frequently. 90003 90002 90006 Long-term oral health 90007 90005 Implants help to preserve bone and prevent gum tissue from shrinking by stimulating them with the forces produced by chewing, which reduces your risk of losing more teeth.Dentures do not have this effect, and an ill-fitting restoration can even accelerate bone loss if it places too much pressure on the gums and underlying bone. 90003 90002 90006 Oral hygiene 90007 90005 Dentures need to be cleaned meticulously every day. In comparison, implants can be maintained by simply brushing and flossing. 90003 90002 90006 Improved appearance 90007 90005 Implants look very natural and function in a way that is similar to your own teeth. Dentures can feel very large and bulky in comparison.90003 90002 90006 Comfort 90007 90005 Dentures often slip around or may click during eating and speaking whereas implants can not move and as they are held rigidly in place by the jawbone. 90003 90002 90006 Food may taste better with implants 90007 90005 It will be easier to chew properly and you should be able to eat a greater variety of food. If they are used to replace upper dentures, you’ll notice food is tastier as your upper palate (which contains thousands of taste buds) will be uncovered.90003 90002 90006 Protecting your natural teeth 90007 90005 Implants help prevent neighboring natural teeth from moving out of position, and they do not require these teeth to be modified in any way. Partial dentures can require neighboring teeth to be modified or ground down. 90003 90009 Cost Comparison 90010 90122 Dentures 90123 90002 The cost of dentures can vary according to where you live and the quality of dentures chosen. While it is possible to purchase cheap dentures, you’ll often find you get what you pay for.High quality restorations use materials and techniques that replicate the appearance of natural gum tissue and teeth. These materials tend to be stronger and longer-lasting and may even include a warranty. 90003 90028 90029 90030 90252 Full Set of Dentures 90032 90037 90038 90039 90030 90041 Basic 90042 90041 $ 600 to $ 1000 90042 90037 90030 90041 Mid-Range 90042 90041 $ 1000. to $ 2000 90042 90037 90030 90041 Premium 90042 90041 $ 4000. to $ 8000 90042 90037 90030 90041 Partial 90042 90041 $ 700 to $ 1800. 90042 90037 90030 90041 Implant Supported 90042 90041 $ 30000 to $ 50000 90042 90037 90120 90121 90002 Add to your site 90003 90002 90006 Basic Quality 90007 90005 For one arch of teeth is typically between $ 300 and $ 500, or an average of $ 1,000 for a complete set of full upper and lower teeth.They usually come with a limited warranty, come in a pre-set size and do not last as long as the higher quality options. 90003 90002 90006 Mid-Range Quality 90007 90005 Replacing one arch costs between $ 500 and $ 1,500, while a full set would be $ 1,000 to $ 3,000. These usually come with a 1-2 year warranty and have a somewhat personalized fit. 90003 90002 90006 Top Quality 90007 90005 Dentures using the best available materials cost $ 2,000 to $ 4,000 per plate or $ 4,000 to $ 8,000 or more for a full set.This includes several follow up visits to ensure a completely personalized, comfortable custom fit and a warranty for 5 to 10 years. 90003 90002 90006 Partial Dentures 90007 90005 Removable partial dentures start at $ 300 to $ 500, but average between $ 700 and $ 1,800. If you have a metal framework then you could end up paying $ 2,000 — $ 4,000 or more. 90003 90122 Dental Implants 90123 90002 They tend to be more expensive than dentures, but the costs depend on your dentist’s experience and popularity, your location, your dental health, the type of implant used, what diagnostic tests are required (x-rays, CT scan, etc.) And whether or not additional procedures such as a bone graft or sinus lift are required. 90003 90002 Other factors to take into consideration include the number of teeth being replaced and the number of implants required as multiple missing teeth can be replaced with a bridge or denture supported by only 2-4 implants. 90003 90002 90006 Single Tooth Implant 90007 90005 It typically costs $ 1,000 to $ 3,000 to have a single tooth implant placed by a dentist. The implant crown will be extra and can cost anywhere from $ 500 to $ 3,000 depending on the materials used.The average cost of a single tooth implant is approximately $ 4,250 but your dentist will be able to give you a more accurate estimate after your initial examination. 90003 90028 90029 90030 90252 Single Tooth Implant Cost 90032 90037 90038 90039 90030 90041 Implant Only 90042 90041 $ 1000. to $ 3000 90042 90037 90030 90041 Abutment & Crown 90042 90041 $ 500 to $ 3000 90042 90037 90030 90041 Average Total Cost 90042 90041 $ 4000 90042 90037 90120 90121 90002 Add to your site 90003 90002 90006 Multiple Implants 90007 90005 The cost of multiple implants can be anywhere from $ 3,500 to $ 30,000 or even more.Two can support a three or four tooth dental bridge, and the average cost of this treatment is approximately $ 8,500. 90003 90002 Add to your site 90003 90002 90006 Implant Supported Dentures 90007 90005 If you wish to replace your upper and lower denture with implant supported dentures or with a fixed bridge, then you can expect to pay anywhere from $ 25,000 right up to $ 95,000, with costs averaging approximately $ 34,000. This is a considerable sum of money, but it is important to remember how many teeth will be replaced during this procedure and that it will require multiple implants.90003 90009 Combination of Both: All-on-4 90010 90002 90367 90367 The All-on-4 technique is used to replace an upper or lower regular denture with a fixed denture that is supported using four implants. 90003 90002 This technique is based on the way the implants are angled, as the two at the front of the mouth are placed at a 90 ° angle, while the two on either side are placed tilted backwards at a 45 ° angle in order to maximize the use of available bone to hold the denture securely in position.This is a specialized technique that requires additional training and planning. 90003 90009 Making a Decision: Dental Implants or Dentures? 90010 90002 Dental implants are largely regarded as the gold standard for replacing missing teeth due to the way they replicate natural tooth roots which helps preserve the jawbone and gum tissue in addition to providing the best aesthetics. In the same vein, dentures can be tricky to wear, restrict your food choices and need to be replaced more frequently.90003 90002 However, there are many situations where dentures are the best option. Implants are not suitable for everybody. Dentures could be the answer if you are opposed to having oral surgery, grind or clench your teeth, can not quit smoking or have a medical condition that significantly increases the risk of implant failure such as diabetes or any disease that compromises your immune system. They are also a great short-term option (several years) if you are currently unable to afford implants.90003 90002 Dentures may seem to be cheaper initially, but a recent study found that implants are a cost-effective option for replacing single teeth. For replacing multiple teeth, implants have higher initial costs but better improvements in oral health-related quality of life compared to other treatment options. 90003 90009 What to Read Next 90010 90009 Over to You 90010 90002 What did you decide was the best option for you? Let us know in the comments why you’re leaning towards implants or dentures.90003.90000 Dental implant vs root canal- Which is best? / Success rates. / Research. 90001 90002 How to make an informed comparison of the two procedures. / Expected success rates. / A checklist of issues to consider. 90003 90002 Using dental implants as a way to replace missing teeth has gained widespread acceptance over the last few decades. And dental patients who are aware of the success of this technique may wonder: 90003 90006 90007 «If my tooth is so damaged that it needs root canal treatment, why not just have it extracted and get a dental implant placed instead?» 90008 90009 90002 90003 90002 We agree, this is a very logical question to have.90003 90014 What needs to be considered when making this decision? 90015 90002 As the remainder of this page outlines, when deciding between the two there are some fundamental issues that must be weighed. They include: 90003 90002 1) What’s the likely success rate of each of the two procedures (research evaluating implants vs. root canals). 90003 90006 90007 How might the specifics of your case affect the expected rates? 90022 90008 90007 How does the dentist’s level of training tend to affect case success? 90008 90009 90002 90003 90002 2) Clinical reasons why one approach might be favored over the other.90003 90006 90007 Case-specific treatment challenges. 90022 90008 90007 Patient’s needs and preferences. 90008 90009 90002 90003 90002 3) Relative cost-effectiveness. 90003 90002 90003 90044 90045 1) Dental implants vs. root canal treatment — Success rates. 90046 90002 Definitively proving which of these treatment options creates a better outcome is difficult. After all, if one of the procedures has been performed, it’s impossible to know what the outcome of the other would have been.90003 90002 However, if the success rate of each is considered independently, they can be compared and you can come up with an answer, at least in general terms. And, for the most part, dental research tends to show that 90050 both treatment approaches can make an excellent choice 90051. 90003 90002 Dental implant vs. root canal treatment. 90003 90055 Dental research. 90056 90014 Study # 1 — 90015 Title: «Endosseous implants versus non-surgical root canal therapy: A systematic review of the literature.»(Blicher 2008) [page references] 90002 This paper reviewed published studies that either … 90003 90061 90007 Evaluated the survival rate of teeth that had received root canal treatment. 90022 90008 90007 Evaluated the success or failure of dental implant placement. 90008 90067 90002 Its findings were … 90003 90006 90007 The success rate for root canal treatment ranged between 92 and 97% (over a time frame of four to eight years) 90022 90008 90007 The success rate for dental implants ranged between 95 and 99% (over a time frame of two to sixteen years).90008 90009 90002 These results suggest that 90078 the overall success rate of either treatment approach is fairly similar 90079, although slightly favoring dental implants. 90003 90014 Study # 2 — 90015 90002 Title: «For teeth requiring endodontic treatment, what are the differences in outcomes of restored endodontically treated teeth compared to implant-supported restorations?» (Iqbal 2007) 90003 90002 This paper, which was also a literature review, took into consideration 55 research studies that had evaluated dental implants and 13 that evaluated root canal therapy.It came to the conclusion that: 90003 90006 90007 90078 No significant differences in survival rates 90079 existed between the two treatment approaches (root canal vs. implants). 90008 90009 90002 The paper continued by stating that a decision between the two should be based on factors other than just the statistical analysis of predicted treatment outcome (success rate). (See lower on this page for an outline of factors that should be considered.) 90003 90014 Study # 3 — 90015 90002 Title: «Outcomes of root canal treatment and restoration, implant-supported single crowns, fixed partial dentures, and extraction without replacement: a systematic review.»(Torabinejad 2007) 90003 90002 This third dental literature review conducted during the same time frame as those above concurred with their findings. 90003 90006 90007 It determined a 97% long-term survival rate for either an extraction / implant or root canal / restore-tooth treatment approach. 90022 90008 90007 The paper went further in stating that either of these approaches could be expected to provide a superior outcome to extracting the tooth and replacing it with a dental bridge. 90008 90009 90002 90003 90014 Conclusions: 90015 90002 Together, the findings of all three of these reviews suggest that 90078 either treatment option (endodontic therapy or implant placement) can make an excellent choice 90079.However, this assumes that a proper standard of care has been practiced (see our next section). 90003 90002 And while there may be specific circumstances why one or the other might make the much better choice in any one situation (see checklist below), as a general rule neither has been universally proven to provide a significant advantage or be the preferred approach. 90003 90055 Root canal vs. implant placement: Which treatment approach do most people prefer? 90056 90002 The Torabinejad (2007) paper mentioned above contains a section that discusses this subject.And it cites a number of sources from which the following statistics are taken. 90003 90006 90007 90% of patients would choose to have root canal treatment again. 88% of patients who have had an implant placed would choose that approach again. 90022 90008 90007 Patient satisfaction ratings for both techniques exceed 90%. 90008 90009 90002 90003 90002 In light of those numbers, it seems safe to say that neither method holds an edge in terms of patient experience or outcome. 90003 90044 90045 2) Maximizing your chances for a successful outcome.90046 90014 a) Pick the proper clinician. 90015 90002 It’s important to understand that different dentists have different levels of training. And with any case, but especially challenging ones, the knowledge and expertise of the clinician can significantly affect the outcome of the work that’s been performed. 90003 90014 i) Clinician success rates for root canal treatment. 90015 90002 A study by Alley (2004) found that 98% of routine cases treated by endodontists (root canal specialists) were successful vs.90% for those treated by general dentists. 90003 90002 [Beyond just increased training and experience, most endodontists incorporate equipment into their practice that general dentists typically just do not have. This includes a surgical operating microscope. 90003 90002 These instruments assist the clinician in identifying any minute root canals that might exist and this aids clinical results. After all, even the most talen 90003.90000 The easy way to implant placement how to manage distance- Styleitaliano 90001 90002 The easy way to implant placement — How to manage distance 90003 90004 Views 11,632 90005 90004 In implant surgery, a correct implant insertion is fundamental in order to obtain optimal aesthetic and functional results that can be maintained over time. 90005 90004 Incorrect positioning of the implants, with regard to the minimum distances from a natural tooth or another implant, would involve a resorption of the interproximal bone crest with loss of the papilla and consequent aesthetic damage, as well as problems from a prosthetic point of view , not guaranteeing the possibility of using crowns of an ideal shape.90005 90004 According to the international literature, the minimum distance between an implant and natural tooth should be at least 1.5-2mm, and between implant and implant should be at least 3mm, in order to obtain an esthetic and functional result lasting in time. 90005 90004 90005 90004 Normally, a wax-up and a surgical guide are used to insert implants in complex cases, but if these are missing, the most common way to measure the distance from the tooth / implant, from which to start to drill the bone, is the use of a conventional periodontal probe, but this procedure is really inaccurate and difficult, if not impossible in some cases, and it entails a waste of intraoperative time.90005 90004 The use of the periodontal probe requires precise calculations, which should take into account the size of the implant to be inserted, the size of the first drill, and the distance that this should have from the neighboring tooth / implant, and obviously a good visibility is necessary to be able to read the measurement on the periodontal probe. 90005 90004 The possibility of reading the measurement from the periodontal probe will depend on the patient’s mouth opening and on the position of the edentulous ridge; moreover, this will always be approximate, not very precise, as it would be impossible to calculate the decimal numbers.90005 90004 Once the ideal position to start the osteotomy has been identified, it is necessary to be maintained during bone perforation and the exact point is sometimes not so easy to see. 90005 90004 All these difficulties for correct implant placement become critical in complex cases, having limited spaces and impassable anatomical limits. The position of the two implants must be as correct as possible, not only from a biological point of view but also from a prosthetic perspective, in order to have an ideal crown position and an optimal aesthetic and functional result.90005 90004 The most expensive, but also the most precise alternative to inserting implants as accurately as possible is the use of a guided surgery, which guarantees very high levels of precision, appropriate in the very complex cases, or a conventional classic surgical template made by the use of a wax-up. 90005 90004 However, surgical templates, despite the benefits offered, are very expensive and therefore their use is not always justified or better, sometimes, they are missed to be prepared.90005 90004 An important help in this difficult and fundamental procedure, and a valid alternative to the two options mentioned above, is provided by Implant Misura space bar, a very useful tool in simple cases which enables to obtain better aesthetic and functional results in an easier, predictable and rapid way, and which becomes a fundamental aid for success in the most complex cases. 90005 90004 This tool helps to identify in an easy and intuitive way the proper position of the first bur to start the bone drilling thus ensuring a correct minimum final distance between the natural tooth and the implant or between two implants, without having to perform complex calculations and intraoperative measurements difficult to read by periodontal probes, and without using expensive surgical guides where not fundamental.Moreover, thanks to the possibility to use different instruments size, it is possible to exploit them in order to position different implants diameters at the desired distance, always respecting the biological limits described in the literature. 90005 90004 90005 90034 90004 Fig.1 90005 90004 Preoperative OPT (90038 1 90039) and intraoral photos (90040 2 90041) of a patient with partial edentulism in the posterior sector of the I quadrant: absence of 1.6 and 1.7 is completely decoronated.90005 90004 Therefore, it was decided to rehabilitate the area by extracting the element 1.7, inserting an immediate post-extraction implant and a conventional implant in the 1.6. 90005 90004 In this case, the available space is limited by the presence of two teeth, mesial and distal, to the edentulous ridge, enhancing the possibility of error and requiring greater precision of insertion and spacing the implants correctly, in order to respect biological limits and obtain adequate aesthetic and functional results with correctly sized crowns.90005 90047 90004 Fig.2 90005 90004 Once the flap is elevated, the decision of where to drill the bone in order to rightly position the implants would not have been so easy with the use of a periodontal probe, especially in this case which was marked by a superior distal surgical site, with reduced visibility and access and the need to position implants in a pre-established space. 90051 The Implant MisuraMRinstrument, in this case, ensures greater simplicity in implant placement and greater accuracy, avoiding the use of a surgical template as it is not essential.90005 90053 90004 Fig.3 90005 90004 The first step is to choose the correct implant diameter and then the corresponding IM-MR instrument. 90005 90004 The instrument has two sides: the first one to distance the implant from the natural root, ensuring 1.5-2mm of distance, the second one to separate the two implants from each other, ensuring the 3mm of distance described in the literature. 90005 90060 90004 Fig.4 90005 90004 The instrument must be placed in close contact with the root of the element 1.5 and then it is possible to start drilling being sure to keep the drill in contact with the instrument if 2.0 mm is the desired minimum distance of the implant from the tooth. 90005 90065 90004 Fig.5 90005 90004 In the same way, the IM-MR instrument was used to control the distance from where to start the bone perforation for the distal implant, by the use of a pin inserted in the first osteotomy as a reference point. 90051 The insertion of the implants is prosthetically guided; therefore the instrument is used to verify that there is a minimum distance of 3mm between the two implants, which will be inserted in the position defined by the future prosthetic crown.90005 90071 90004 Fig.6 90005 90004 The post-operative panoramic X-ray demonstrates the correct positioning of the implants and the precise distance between them. 90051 The IM-MR instrument was fundamental to obtain this result in a quick and simple way, facilitating and speeding up all the surgical procedures, guaranteeing the highest levels of precision. Without the measuring instrument, it would have been extremely complex to insert implants with such precision and simplicity, due to problems of visibility and access.90005 90077 90004 Fig.7 90005 90004 Dr. Marco Redemagni and the Styleitaliano team, designed, together with LM, this set of implant spacers. Available with LM local dealer or online store of Smile Line by Styleitaliano webshop. 90005 90082 Conclusions 90083 90004 90005 90004 For the correct insertion of implants, both in simple and complex cases, it is important to maintain a minimum distance between implants (3 mm) and between the implant and an adjacent tooth (1.5-2 mm) in order to maintain an adequate interproximal bone crest and therefore the possibility of having a natural papilla, as well as having the possibility of prosthesizing implants with adequate size crowns; all this to guarantee the patient an optimal functional aesthetic result.90005 90004 In simple cases, but even more so in complex cases, it is a great advantage to have an instrument that allows to distance and stabilize the first drill for bone perforation from the tooth / implant, simply and quickly, without the need for complex calculations , and that can be exploited in complete safety even in sites with reduced visibility, ensuring correct insertion of the system while maintaining all the minimum distances required. 90005 90004 This tool makes the whole procedure much simpler but, at the same time, more precise and faster, thus ensuring optimal aesthetic and functional results without necessarily having to resort to the use of surgical masks if not necessary.90005 90004 90005 90082 Bibliography 90083 90004 90005 90098 90099 90004 Salama H, Salama M, Garber D, Adar P: «The interproximal height of bone: a guidepost to predictable aesthetic strategies and soft tissue contours in anterior tooth replacement.» Pract Periodont Aesthet Dent 1998; 10 (9): 1131-1141 90005 90102 90099 90004 Tarnow DP, Cho SC, Wallace SS: «The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of the inter-implant bone crest» J Periodontol 2000; 71: 546-54 90005 90102 90099 90004 Cardarapoli G, Wennstr Öm JL, Lekholm U: «Peri-implant bone alterations in relation to inter-unit distances.A 3 year retrospective study. » Clin Oral Impl Res 2003; 14: 430-436 90005 90102 90111 .90000 Risks and Complications of Breast Implants 90001 90002 Risks of Breast Implants 90003 90004 Some of the complications and adverse outcomes of breast implants include: 90005 90004 90007 Breast Implants — Certain Labeling Recommendations to Improve Patient Communication Draft Guidance 90008 90005 90004 The draft guidance, Breast Implants — Certain Labeling Recommendations to Improve Patient Communication, provides recommendations for the form and content for certain labeling information for saline and silicone gel-filled breast implants, including: 90005 90012 90013 Boxed warning 90014 90013 Patient decision checklist 90014 90013 Materials / device descriptions, including types and quantities of chemicals and heavy metals found in or released by breast implants 90014 90013 Silicone gel-filled breast implant rupture screening recommendations 90014 90013 Patient device card 90014 90023 90004 When final, the recommendations in this guidance will supplement or, in some cases, replace recommendations in the FDA’s Saline, Silicone Gel, and Alternative Breast Implants guidance, issued November 17, 2006.90005 90026 90002 Implant Complications 90003 90004 The following is a list of local complications and adverse outcomes that occur in at least 1 percent of breast implant patients at any time. You may need non-surgical treatments or additional surgeries to treat any of these, and you should discuss any complication and necessary treatment with your doctor. These complications are listed alphabetically, not in order of how often they occur. 90005 90031 90032 90033 90034 Complication 90035 90034 Description 90035 90038 90039 90040 90033 90042 90007 Asymmetry 90008 90045 90042 The breasts are uneven in appearance in terms of size, shape or breast level.90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Breast Pain 90008 90045 90042 Pain in the nipple or breast area 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Breast Tissue Atrophy 90008 90045 90042 Thinning and shrinking of the skin 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Calcification / Calcium Deposits 90008 90045 90042 Hard lumps under the skin around the implant. These can be mistaken for cancer during mammography, resulting in additional surgery. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Capsular Contracture 90008 90045 90042 Tightening of the tissue capsule around an implant, resulting in firmness or hardening of the breast and squeezing of the implant if severe.90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Chest Wall Deformity 90008 90045 90042 Chest wall or underlying rib cage appears deformed. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Deflation 90008 90045 90042 Leakage of the saltwater (saline) solution from a saline-filled breast implant, often due to a valve leak or a tear or cut in the implant shell (rupture), with partial or complete collapse of the implant. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Delayed Wound Healing 90008 90045 90042 Incision site fails to heal normally or takes longer to heal.90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Extrusion 90008 90045 90042 The skin breaks down and the implant appears through the skin. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Hematoma 90008 90045 90042 Collection of blood near the surgical site. May cause swelling, bruising and pain. Hematomas usually occur soon after surgery, but can occur any time there is injury to the breast. The body may absorb small hematomas, but large ones may require medical intervention, such as surgical draining. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Iatrogenic Injury / Damage 90008 90045 90042 Injury or damage to tissue or implant as a result of implant surgery 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Infection, including Toxic Shock Syndrome 90008 90045 90042 Occurs when wounds are contaminated with microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi.Most infections resulting from surgery appear within a few days to a week, but infection is possible any time after surgery. If an infection does not respond to antibiotics, the implant may need to be removed 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Inflammation / Irritation 90008 90045 90042 Response by the body to an infection or injury. Demonstrated by redness, swelling, warmth, pain and or / loss of function. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Lymphedema or Lymphadenopathy 90008 90045 90042 Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Malposition / Displacement 90008 90045 90042 The implant is not in the correct position in the breast.This can happen during surgery or afterwards if the implant moves or shifts from its original location. Shifting can be caused by factors such as gravity, trauma or capsular contracture. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Necrosis 90008 90045 90042 Dead skin or tissue around the breast. Necrosis can be caused by infection, use of steroids in the surgical breast pocket, smoking, chemotherapy / radiation, and excessive heat or cold therapy. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Nipple / Breast Sensation Changes 90008 90045 90042 An increase or decrease in the feeling in the nipple and / or breast.Can vary in degree and may be temporary or permanent. May affect sexual response or breast feeding. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Palpability 90008 90045 90042 The implant can be felt through the skin. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Ptosis 90008 90045 90042 Breast sagging that is usually the result of normal aging, pregnancy or weight loss. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Redness / Bruising 90008 90045 90042 Bleeding at the time of surgery can cause the skin to change color.This is an expected symptom due to surgery, and is likely temporary. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Rupture 90008 90045 90042 A tear or hole in the implant’s outer shell. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Seroma 90008 90045 90042 Collection of fluid around the implant. May cause swelling, pain and bruising. The body may absorb small seromas. Large ones will require a surgical drain. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Skin Rash 90008 90045 90042 A rash on or around the breast.90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Unsatisfactory Style / Size 90008 90045 90042 Patient or doctor is not satisfied with the overall look based on the style or size of the implant used. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Visibility 90008 90045 90042 The implant can be seen through the skin. 90045 90038 90033 90042 90007 Wrinkling / Rippling 90008 90045 90042 Wrinkling of the implant that can be felt or seen through the skin. 90045 90038 90249 90250 90004 A complete list of complications, as well as information on rates for those complications can be found in the patient labeling for the approved breast implants, Labeling for Approved Breast Implants.90005 90026 90002 Additional Surgeries 90003 90004 Breast implants are not lifetime devices. The longer you have breast implants, the more likely it is that complications will occur and you will need to have them removed. There is no guarantee that you will have a satisfactory cosmetic outcome from any reoperation. 90005 90004 The type of surgical procedure performed during a reoperation depends on the complication involved. You may need to have one or more reoperations over the course of your life due to one complication or a combination of local complications.More than one procedure may be performed in a single reoperation. Types of surgical procedures that may be performed in a reoperation include: 90005 90012 90013 Implant removal, with or without replacement 90014 90013 Capsule removal or surgical release of the scar tissue around the breast implant 90014 90013 Scar or wound revision, such as surgical removal of excess scar tissue 90014 90013 Drainage of a hematoma by inserting a needle or tube through the skin to drain the collection of blood 90014 90013 Repositioning of the implant by surgically opening the incision and moving the implant 90014 90013 Biopsy / cyst removal by inserting a needle through the skin or cutting through the skin to remove a lump.90014 90023 90026 90002 Implant Removal Options 90003 90004 If you elect to have your breast implants removed, or if it is medically indicated, there are two primary methods for implant removal. Your plastic surgeon may choose to remove your implant alone and leave the scar tissue that surrounds your implant in your body, also called the scar capsule. This option requires less surgical dissection and may pose less risk of local complications such as bleeding. Alternatively, your surgeon may also surgically remove the scar capsule when your breast implant is removed.This is called «en-bloc resection». You should discuss with your surgeon which method is best for your situation. 90007 90008 90005 90004 If you experience any symptoms of BIA-ALCL, such as persistent swelling or pain, or other changes in the area around your breast implant, talk to your surgeon or health care provider about the need for further evaluation. Evaluation for BIA-ALCL typically involves a physical exam, imaging, and / or assessment of the fluid or tissue around the breast implant.It is important to have an evaluation to diagnose BIA-ALCL because a confirmed BIA-ALCL diagnosis may change the type of operation that should be performed. 90005 90004 Generally, patients with confirmed BIA-ALCL should undergo implant removal and removal of the surrounding scar capsule, which is a more extensive operation than implant removal alone. Talk to your surgeon about the method of removal most appropriate for you. 90005 90004 Removal of a breast implant, with or without replacement, is one type of reoperation.The life of breast implants varies by person and can not be predicted. You may need to have your implant removed at some time over the course of your life because of one or more local complications. 90005 90004 After removal, some women do not choose to replace their implants. These women may have cosmetically undesirable dimpling, puckering, or sagging of their natural breasts. 90005 90004 The photograph below shows a 29-year-old woman 1 year after having her silicone gel-filled breast implants removed, but not replaced.Women with large breast implants, especially those inserted on top of the chest muscles (subglandularly), may have major cosmetic deformity if they choose not to replace them or to undergo additional reconstructive surgery. 90005 90004 90292 90293 Photo courtesy of Walter Peters, Ph.D., M.D., F.R.C.S.C., University of Toronto. 90294 90005 90004 Some insurance companies do not cover implant removal or implant replacement, even if there are complications and even if the first implant surgery was covered.90005 90026 90002 Capsular Contracture 90003 90004 Capsular contracture is the hardening of the breast around the implant. It can occur in the tissue surrounding one or both implants. This hardening causes the tissue to tighten, which can be painful. 90005 90004 Capsular contracture may be more common following infection, hematoma and seroma. However, the cause of capsular contracture is not known. 90005 90004 There are four grades of capsular contracture, known as Baker grades. 90005 90004 90007 Baker Grading Scale 90008 90005 90012 90013 90007 Grade I: 90008 Breast is normally soft and looks natural 90014 90013 90007 Grade II: 90008 Breast is a little firm but looks normal 90014 90013 90007 Grade III: 90008 Breast is firm and looks abnormal 90014 90013 90007 Grade IV: 90008 Breast is hard, painful, and looks abnormal 90014 90023 90004 Grades III and IV capsular contracture are considered severe and may require reoperation.The surgical procedure usually involves removal of the implant with or without replacement of the implant. There is a possibility that capsular contracture could occur again after surgery to correct it. 90005 90004 The FDA has not cleared or approved any devices to treat or reduce the incidence of capsular contracture. 90005 90004 The picture below shows a Grade IV capsular contracture in the right breast of a 29-year-old woman 7 years after placement of silicone gel-filled breast implants.90005 90004 90292 90293 Photo courtesy of Walter Peters, Ph.D., M.D., F.R.C.S.C., University of Toronto. 90294 90005 90026 90002 Rupture and Deflation 90003 90004 Rupture is a tear or hole in the outer shell of the breast implant. 90005 90004 Some possible causes of rupture of breast implants include: 90005 90012 90013 Capsular contracture 90014 90013 Compression during a mammogram 90014 90013 Damage by surgical instruments 90014 90013 Damage during procedures to the breast, such as biopsies and fluid drainage 90014 90013 Normal aging of the implant 90014 90013 Overfilling or underfilling of saline-filled breast implants 90014 90013 Physical stresses such as trauma or intense physical pressure 90014 90013 Placement through a non-FDA approved incision site, for example the belly button 90014 90013 Too much handling during surgery 90014 90023 90026 90002 Saline-Filled Breast Implant Rupture and Deflation 90003 90004 The term rupture is used for all types of breast implants, but the term deflation is only used for saline-filled implants.You and / or your doctor will be able to tell if your saline-filled implant ruptures because the saline solution leaks into your body immediately or over several days and deflates the implant. You will notice that your implant loses its original size or shape. 90005 90004 The following surgical procedures are 90007 not 90008 recommended for FDA-approved saline-filled breast implants because they are known to cause rupture and deflation: 90005 90012 90013 Closed capsulotomy — a technique used to relieve capsular contracture involving manually squeezing the breast to break the hard capsule 90014 90013 Placement of drugs or other substances inside the implant other than sterile saline 90014 90013 Any contact of the implant with Betadine, a povidone-iodine topical antiseptic made by Purdue Frederick Company 90014 90013 Injection through the implant shell 90014 90013 Alteration of the implant 90014 90013 Stacking of the implants (more than one implant per breast pocket).90014 90023 90004 The photograph below shows a 30-year-old woman whose left saline-filled breast implant deflated. The implant is thought to have deflated due to a particular design, which is no longer used by the manufacturer. 90005 90004 90292 90293 Photo courtesy of Walter Peters, Ph.D., M.D., F.R.C.S.C., University of Toronto. 90294 90005 90026 90002 Silicone Gel-Filled Implant Rupture 90003 90004 Silicone breast implants can rupture at any time after your implant surgery, but the longer an implant is in place, the greater the possibility an implant may rupture.90005 90004 If a silicone gel-filled breast implant ruptures, it is not likely that you or your doctor will immediately notice because most silicone implant ruptures are without symptoms, «silent ruptures». A silent rupture does not change the way an implant looks or feels, and your surgeon or health care provider may not be able to detect a silent rupture by a physical examination alone. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most effective method for detecting silent rupture of silicone gel-filled breast implants.90005 90004 However, occasionally when a silicone gel-filled implant ruptures, a woman may notice a decrease in breast size, change in breast implant shape, hard lumps over the implant or chest area, an uneven appearance of the breasts, pain or tenderness, tingling , swelling, numbness, burning, or changes in sensation. 90005 90004 Generally, when silicone gel-filled implants rupture, the silicone gel escapes through a tear or hole in the implant shell but remains confined within the scar tissue capsule around the implant, called an intra-capsular rupture.If the gel migrates beyond the scar tissue around the breast implant, it is called an extracapsular rupture. Sometimes, after a rupture, the gel may move to other distant areas around the body, which is called extracapsular rupture with gel migration. It may be difficult to remove silicone gel after a rupture. 90005 90026 90002 Connective Tissue Disease, Breast Cancer, and Reproductive Problems 90003 90004 The FDA has not detected any association between silicone gel-filled breast implants and connective tissue disease, breast cancer, or reproductive problems.However, the FDA has received reports of systemic symptoms (see below) by some patients with both saline and silicone gel-filled breast implants. In order to fully understand these complications, studies would need to be larger and longer than those conducted so far. 90005 90026 90002 Systemic Symptoms [Breast Implant Illness (BII)] 90003 90004 Symptoms such as fatigue, memory loss, rash, «brain fog,» and joint pain may be associated with breast implants. Some patients may use the term «breast implant illness» (BII) to describe these symptoms.Researchers are investigating these symptoms to better understand their origins. These symptoms and what causes them are poorly understood. In some cases, removal of the breast implants without replacement is reported to reverse symptoms of breast implant illness. 90005 90004 We encourage patients to report any injury, adverse event, or symptom related to a medical device, including the symptoms listed above, to the FDA by phone at 1-800-FDA-1088 or online at MedWatch, the FDA Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting program.Please include the following information: 90005 90012 90013 Device Name (Brand Name) 90014 90013 Manufacturer’s Name 90014 90013 Details of Adverse Event and Medical and / or Surgical Interventions (if applicable) 90014 90023 90026 90002 Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) 90003 90004 Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) is a T-cell lymphoma that can develop following breast implants. For additional information, see: Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL).90005 90026 90002 Breastfeeding 90003 90004 Some women who undergo breast augmentation can successfully breastfeed and some can not. Women who undergo mastectomies and then have breast implant reconstruction surgeries may not be able to breastfeed on the affected side due to loss of breast tissue and the glands that produce milk. 90005 90026 90002 Effects on Children 90003 90004 At this time, it is not known if a small amount of silicone may pass through from the breast implant silicone shell into breast milk during breastfeeding.Although there are currently no established methods for accurately detecting silicone levels in breast milk, a study measuring silicon (one component in silicone) levels did not indicate higher levels in breast milk from women with silicone gel-filled implants when compared to women without implants. 90005 90004 In addition, concerns have been raised regarding potential damaging effects on children born to mothers with implants. Two studies in humans have found no increased risk of birth defects in children born to mothers who have had breast implant surgery.Although low birth weight was reported in a third study, other factors (for example, lower pre-pregnancy weight) may explain this finding. 90005 .